Standard electrode potentials are Fe2+/Fe; E° = 0.44 volts Fe3+/Fe2+; E° = 0.77 volts Fe2+, Fe3+ and Fe blocks are kept together, then (1) Fe2+ increases (2) Fe3+ decreases (3) Fe2+/Fe3+ remains unchanged (4) Fe2+ decreases

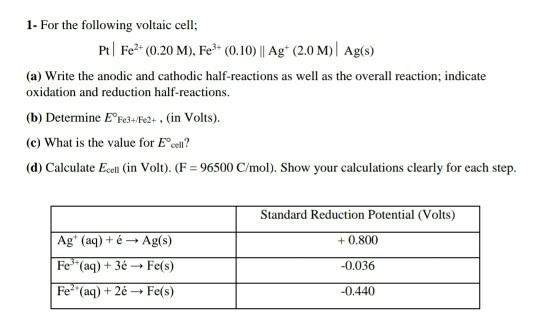
Given standard electrode potentials: Fe^3 + + 3e^-→ Fe;E^0 = - 0.036V Fe^2 + + 2e^-→ Fe;E^0 = - 0.440V The standard electrode potential E^o for Fe^3 + + e^ - → Fe^2 + is:

Given electrode potentials are : Fe^3 + + e^- → Fe^2 + ; E^ = 0.771 V I2 + 2e^- → 2I^ ; E^ = 0.536 V Find the E^ cell for the cell reaction: 2Fe^3 + + 2I^ → 2Fe^2 + + I2 is :
The standard reduction potentials of the Fe3+/Fe2+ and Fe2+/Fe couples are 0.77 and 0.44 V, respectively. The standard reduction potential (in V) for the Fe3+/Fe couple is _______Correct answer is '-0.03'. Can
Fe3+(aq) + e– → Fe2+(aq), E° = +0.77 V Cl2(g) + 2e– → 2Cl–(aq), E° = +1.36 V Write the reaction which could be feasible using above half cells.








![Solved Electochemistry How can I find [Fe2+] , [Fe3+] | Chegg.com Solved Electochemistry How can I find [Fe2+] , [Fe3+] | Chegg.com](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media%2Fab8%2Fab8bf5bc-6985-419c-84d0-156f024c006b%2FphpBxTTTs.png)